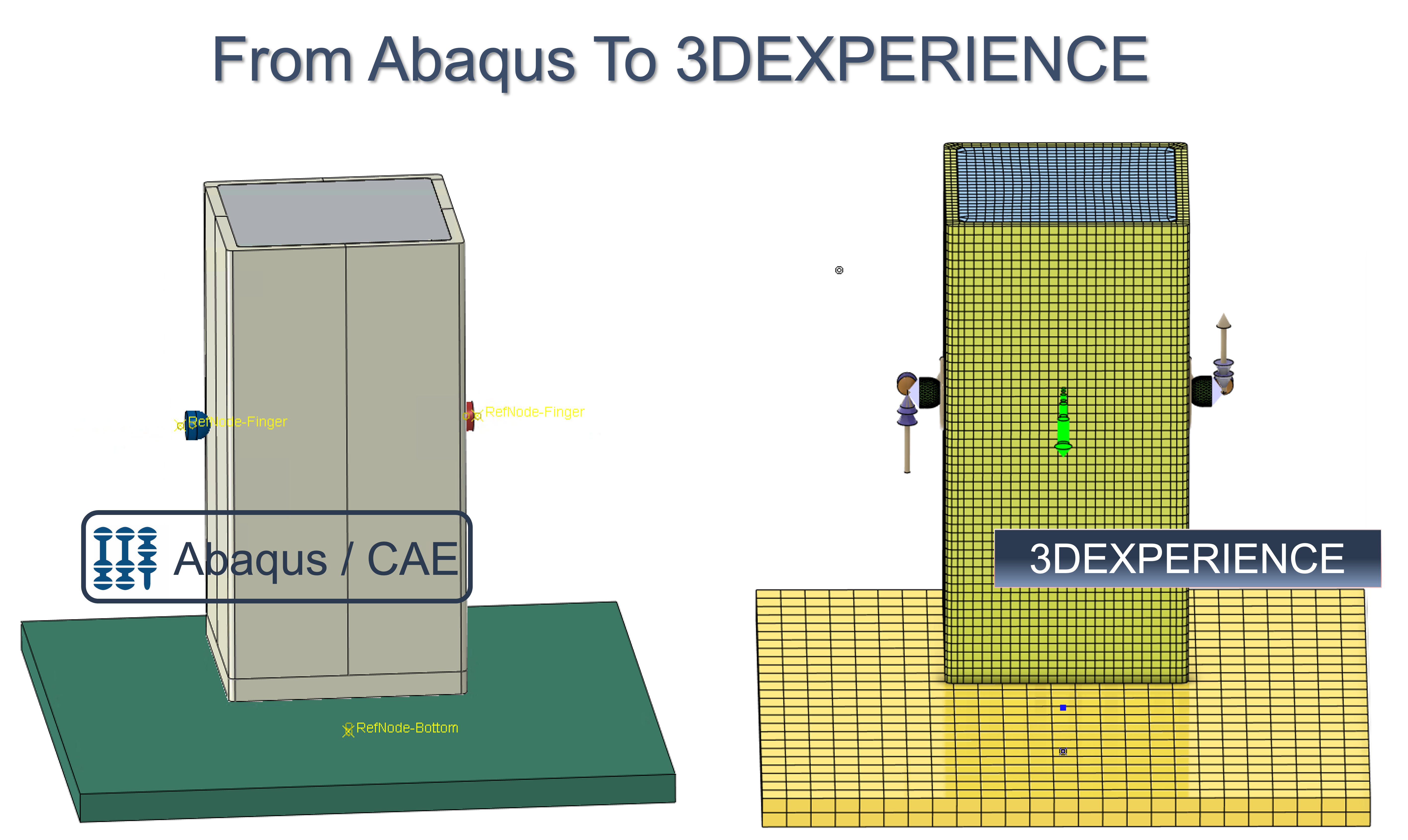
In finite element analysis, Abaqus/CAE and Abaqus/Viewer are the standard pre- and post-processors for Dassault Systèmes finite element program system Abaqus. The integration of Abaqus functionalities in Abaqus/CAE has reached a very high level.
If the user wants to switch from Abaqus/CAE to the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, the question arises as to what extent accustomed and proven working methods can be transferred from one system to the other.
Our wiki posts with the overarching title ‘From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE’ is designed to help users make this transition. However, we also want to highlight the advantages of 3DEXPERIENCE.
Even if we will not be able to cover all areas, we want to work with several contributions due to the volume of material:
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – General remarks
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – Geometry
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – Materials
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – Sets, Meshing, Properties
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – Assembly Sets, Constraints
- From Abaqus To 3DEXPERIENCE – Procedures, Steps, Loads, Boundary Conditions
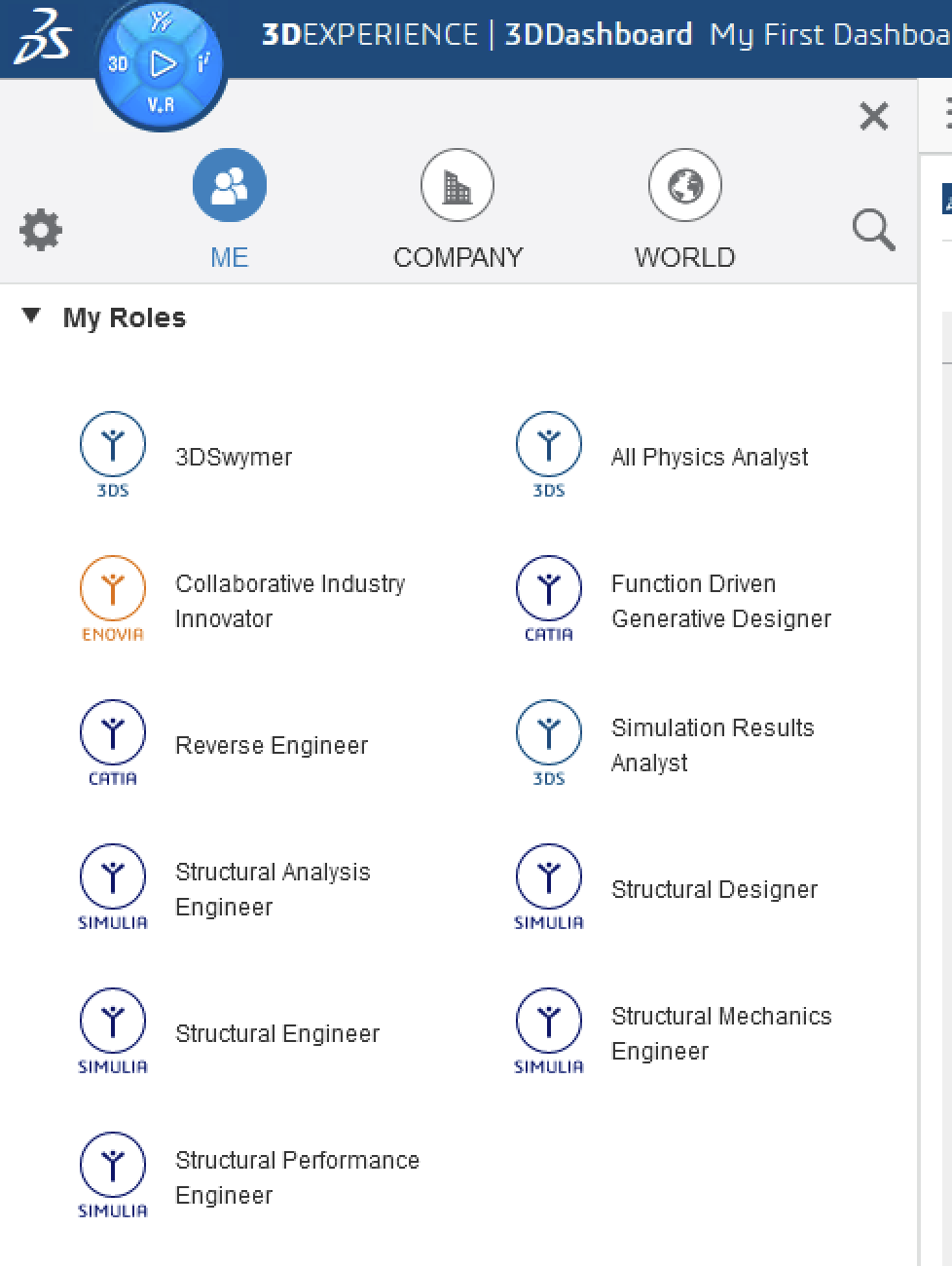
If on the one hand it is only Abaqus/CAE, then in 3DEXPERIENCE you work with user roles to which apps are assigned. Here, the different roles for simulation can be roughly divided into roles for designers and roles for simulation specialists. To see which roles are assigned to a user, click the compass.
Thus, the roles of Structural Designer, Structural Engineer and Structural Performance Engineer are more related to design-integrated simulation, see also [1].
The roles Structural Mechanics Engineer and Structural Analysis Engineer are then more likely to be assigned to the simulation expert, see also [2] and [3].
The All Physics Analyst is a special role which allows, for example, the connection of Abaqus/CAE to the platform or the execution of externally generated simulation jobs.
There are also other special roles, but we will not go into these here.
3DEXPERIENCE contains a variety of different roles and functionalities. Among the authoring systems, the CATIA and SIMULIA brands provide the apps for geometric design and numerical simulation. The image below shows the main apps for creating geometries and calculation models for the simulation engineer. Here, the check mark indicates the apps that correspond to authoring systems and are performed locally on the client computer.
Since the design-integrated simulation roles assume that the designer already has apps for geometry creation, the geometry creation and editing apps are not attached to these roles.
When choosing the “right” roles and apps, please ask your reseller or even us for advice.
In Abaqus/CAE you create a model. All necessary information and definitions are stored in this. A job is then used for the execution.
In 3DEXPERIENCE, you create a Physical Product for the component. This contains the geometry, material and meshing as well as definitions of groups (sets). A Physical Product is also used for an Assembly. By using the Scenario App, the Physical Product is merged with a Scenario as well as the results of calculations.
The representation of the (structure) tree differs from the one used in Abaqus/CAE and is more similar to the tree used in CATIA, see picture below. The tree can be made permanently visible or is unfolded as needed.
The image below shows the tree of a Physical Product on the left and a Scenario with Physical Product on the right. We will explain how these products and scenarios are stored in a separate wiki post.
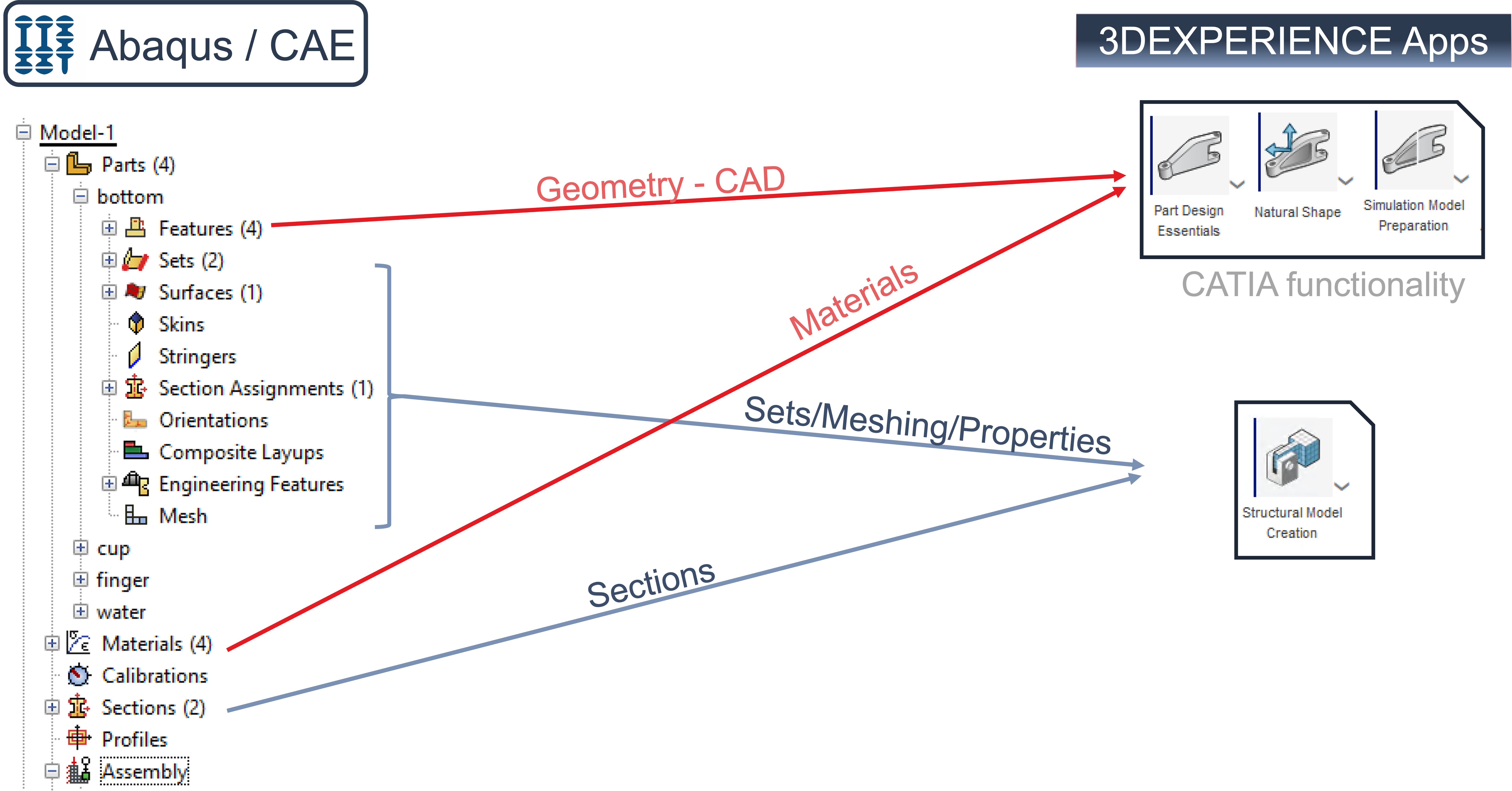
In Abaqus/CAE the model splits into two essential blocks, lower left image:
- Parts – with the components, the properties, the materials and the meshing
- Assembly – with the assembly of the various instances of the Parts, as well as definitions of Contact, Constraints, Loads, and Boundary Conditions.
The meshing of an independent instance can also be done in the assembly. Assemblies of other models can also be adopted. However, neither is considered here.
In 3DEXPERIENCE, the Part Design Essential and Natural Shape apps are used for geometry generation, lower image on the right. The Simulation Model Preparation app can be used to edit the geometry, such as defeaturing or partioning. The Structural Model Creation app is used to define sets, meshing, properties and sections.
To create the assembly, you start in Abaqus/CAE by creating instances of the parts and positioning them. Then the steps, output, interaction, constraints, loads and boundary conditions are defined, lower left image.
In 3DEXPERIENCE, the assembly of the components is done in the Assembly Design app. The definition of sets or constraints for the assembly is done with the Structural Model Creation app. In the Mechanical Scenario Creation app, the steps, output, interaction, loads and boundary conditions are then defined, lower image on the right.
In part, this text and illustrations shown are based on research of evaluated literature. If this is the case, the sources are marked in the text by a number, e.g. [2], and the source is listed here.
In part, however, the sources listed here should simply be understood as recommendations for further reading.